
Mole/Skin Tags/Wart/Lesion Removal
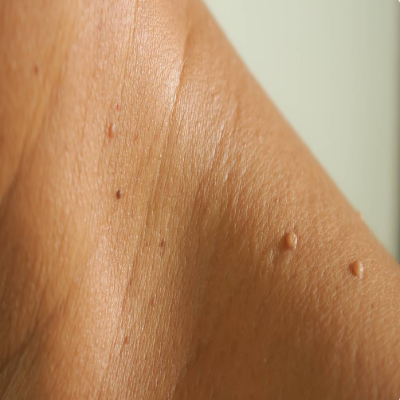
Removing moles, skin tags, warts, and lesions is a common dermatological procedure aimed at addressing unwanted skin growths. Each type of growth has its characteristics, and the removal methods can vary based on the specific type, size, location, and any associated symptoms. Here’s an overview of these procedures:
Types of Skin Growths
Moles (Nevus)
- Description: Moles are generally benign growths that can appear anywhere on the body, varying in color from brown to black. They can be flat or raised and may have hair.
- Reason for Removal: Moles may be removed for cosmetic reasons, irritation from clothing, or if there are changes in size, shape, or color that raise concerns about skin cancer.
Skin Tags (Acrochordon)
- Description: Skin tags are small, soft, benign growths that hang off the skin. They commonly appear in areas where skin rubs against skin or clothing, such as the neck, armpits, or eyelids.
- Reason for Removal: Removal is typically for cosmetic reasons, discomfort, or if they become irritated.
Warts (Verrucae)
- Description: Warts are benign growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can occur anywhere on the body and may be flesh-colored, white, or brown.
- Reason for Removal: Warts may be removed for cosmetic reasons, if they are painful, or if they spread to other areas.
Lesions
- Description: Lesions can refer to any abnormal area of skin, including cysts, growths, or patches that can be benign or indicative of skin conditions (e.g., actinic keratosis).
- Reason for Removal: Lesions are often removed for biopsy to rule out cancer, cosmetic reasons, or if they are symptomatic.
Removal Methods
Surgical Excision
- Description: This method involves cutting out the growth along with a margin of healthy skin. It’s often used for moles, large warts, or suspicious lesions.
- Advantages: Allows for thorough examination of the tissue for signs of cancer and is effective for larger growths.
- Disadvantages: Requires stitches and may leave a scar.
Cryotherapy
- Description: This technique involves freezing the growth with liquid nitrogen, causing the tissue to die and eventually fall off. It is commonly used for warts and some skin lesions.
- Advantages: Quick, minimally invasive, and effective for superficial growths.
- Disadvantages: May require multiple sessions; potential for blistering or pigmentation changes.
Electrosurgery
- Description: This method uses electrical currents to burn off the growth. It is often employed for skin tags and some warts.
- Advantages: Effective for small growths and results in minimal bleeding.
- Disadvantages: May cause minor scarring and requires local anesthesia.
Laser Therapy
- Description: High-intensity light beams are used to vaporize the growth. It is effective for various types of skin lesions and moles.
- Advantages: Precise and minimizes damage to surrounding skin; often leads to less scarring.
- Disadvantages: May require multiple sessions and can be more expensive.
Topical Treatments
- Description: Certain topical medications can be used to treat warts (e.g., salicylic acid) and some benign lesions.
- Advantages: Non-invasive and can be done at home.
- Disadvantages: Requires consistent application over time and may not be effective for all types of growths.
What to Expect During Removal
Consultation: A dermatologist will assess the growth, discuss the need for removal, and recommend the most suitable method.
Preparation: The area will be cleansed, and local anesthesia may be administered to minimize discomfort.
Procedure: The chosen removal method will be performed. The duration and complexity depend on the growth’s size and type.
Post-Procedure Care: Instructions will be given on how to care for the area, including keeping it clean and dry and when to return for follow-up.
Aftercare and Recovery
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently wash the area and keep it dry to prevent infection.
- Avoid Picking or Scratching: This can lead to scarring or infection.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Look for increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Follow-Up: Attend any recommended follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
- Scarring: Some procedures may leave scars, depending on the method and size of the growth.
- Infection: There is a risk of infection if proper care isn’t taken.
- Recurrence: Some growths, particularly warts, may recur after treatment.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice any changes in a mole or skin growth (such as changes in color, size, or shape), experience discomfort, or have concerns about a lesion, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.